The 2001 Honda CR-V, equipped with a reliable inline-four B20Z2 engine, relies on a precise firing order for smooth operation and balanced power delivery. This guide breaks down the firing order, explains its importance, and outlines key considerations in a clear, actionable format.

Quick Navigation
What is the Firing Order?
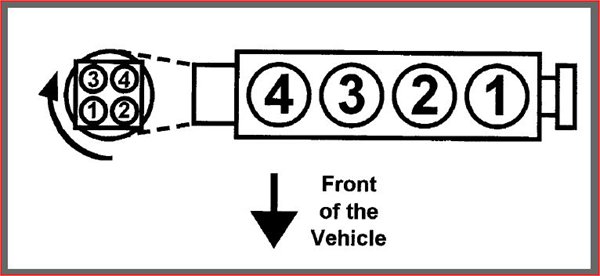
The firing order is the specific sequence in which an engine’s cylinders ignite. It ensures smooth power delivery and efficient operation. The firing order for the 2001 Honda CR-V is 1-3-4-2
How It Works
- Cylinder 1 fires first.
- Cylinder 3 fires second.
- Cylinder 4 fires third.
- Cylinder 2 fires fourth.
The sequence repeats, maintaining continuous operation.
Why the Firing Order Matters
- Engine Smoothness: The proper firing order prevents vibrations and ensures balanced operation.
- Power Distribution: Correct sequencing delivers consistent power to the crankshaft.
- Fuel Efficiency: Efficient combustion reduces energy waste and improves mileage.
- Troubleshooting: Understanding the firing order simplifies misfire diagnosis and repair.
Engine Layout and Cylinder Numbering
The B20Z2 inline-four engine uses a simple layout. Its cylinders are arranged in a straight line, numbered sequentially from the timing belt side:
- Cylinder 1: Closest to the timing belt.
- Cylinder 2: Second from the timing belt.
- Cylinder 3: Third from the timing belt.
- Cylinder 4: Furthest from the timing belt.
This numbering is essential for identifying issues or replacing components.
Components Involved in Firing
- Crankshaft: Converts piston motion into rotational energy.
- Camshaft: Regulates valve timing for air-fuel intake and exhaust.
- Ignition Coil: Generates high-voltage sparks for combustion.
- Distributor (or ECU): Manages ignition timing and sequencing.
- Spark Plugs: Ignite the air-fuel mixture in each cylinder.
Each part must function perfectly to maintain the firing order.
Firing Order Function in the 2001 Honda CR-V
The inline-four engine operates using a four-stroke cycle:
- Intake Stroke: Cylinder draws in air-fuel mixture.
- Compression Stroke: Mixture compresses before ignition.
- Power Stroke: Spark ignites the mixture, pushing the piston down.
- Exhaust Stroke: Cylinder expels exhaust gases.
Each cylinder fires once during the four-stroke cycle, with power delivery alternating to maintain balance.
Common Issues with Firing Order
Misfires: Disrupted firing causes uneven combustion.
- Symptoms: Rough idle, reduced power, higher emissions.
- Causes: Worn spark plugs, faulty ignition coils, or incorrect timing.
Power Loss: Incorrect firing reduces engine efficiency.
- Solution: Verify ignition system functionality.
Vibrations: Improper firing order leads to unbalanced operation.
- Diagnosis: Inspect timing and ignition components.
Engine Knock: Faulty timing causes premature combustion.
- Prevention: Use proper fuel and ensure timing is correct.
How to Check the Firing Order
- Consult the Manual: Verify the firing order in the service manual.
- Inspect the Distributor: Ensure wires are routed correctly to each cylinder.
- Test Ignition Components: Check spark plugs and coils for proper function.
- Use a Diagnostic Tool: OBD-II scanners detect misfire-related codes.
- Perform a Cylinder Balance Test: Ensure all cylinders contribute equally.
Adjusting the Firing Order
The firing order in the 2001 Honda CR-V cannot be changed without redesigning the engine. However, ensuring proper ignition timing and component functionality is key to maintaining the factory firing order:
- Distributor Timing: Adjust the position if timing is off.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Use correct plugs and gap them properly.
- Ignition Coil Testing: Ensure voltage delivery matches cylinder needs.
- Timing Belt Alignment: Keep camshaft and crankshaft synchronized.
Troubleshooting Firing Order Problems
- Check Spark Plugs: Inspect for wear, fouling, or improper gaps.
- Inspect Ignition Wires: Ensure correct routing and continuity.
- Test the Distributor Cap: Look for cracks or carbon tracking.
- Verify Timing Belt Position: Misalignment can disrupt firing order.
- Listen for Engine Noises: Knocking or pinging suggests timing issues.
Maintenance Tips for Firing Order Reliability
- Replace Spark Plugs Regularly: Prevent misfires by following manufacturer recommendations.
- Inspect Ignition Wires: Replace damaged or frayed wires.
- Check Distributor Condition: Ensure the cap and rotor function correctly.
- Maintain the Timing Belt: Replace at recommended intervals to prevent skipping.
- Use Quality Fuel: Avoid buildup in the combustion chambers.
Performance Considerations
- Tuning: Retain the factory firing order for reliable performance during tuning.
- Aftermarket Ignition Systems: Enhance spark efficiency with performance-grade components.
- Cylinder Compression Testing: Confirm even compression across all cylinders for optimal firing.
Summary of Key Points
- Firing Order: 1-3-4-2.
- Engine Layout: Inline-four with sequential cylinder numbering from the timing belt.
- Common Issues: Misfires, vibrations, power loss, and engine knock.
- Components Involved: Crankshaft, camshaft, ignition coil, distributor, spark plugs.
- Maintenance Essentials: Replace spark plugs, inspect ignition wires, maintain the timing belt.
Engines with Similar Firing Orders
- 2004 Honda Civic Firing Order
- 2010 Honda Odyssey Firing Order
- 2000 Honda CR V Firing Order
- Honda K24 Firing Order
- Honda J Series Firing Order
Final Thoughts
The 2001 Honda CR-V firing order (1-3-4-2) is a fundamental aspect of its engine design. Proper maintenance and understanding of this sequence ensure smooth operation, efficient combustion, and reliable performance. By addressing ignition system health and timing accuracy, you can prevent common issues and keep your CR-V running efficiently. Whether for daily driving or advanced tuning, respect the integrity of the firing order for optimal results.

