The Mazda 3, a compact car known for its sleek design, efficient performance, and responsive handling, is equipped with a well-engineered engine that depends on proper ignition timing. Central to its smooth operation is the firing order, the sequence in which the engine’s cylinders fire.
This guide explores the Mazda 3 firing order, its importance, common issues, and tips for maintenance, all in an easy-to-follow, conversational tone.

Quick Navigation
What Is the Firing Order?
The firing order refers to the sequence in which an engine’s cylinders ignite the air-fuel mixture to produce power. In the Mazda 3, equipped with an inline-4 engine (commonly found in models like the SkyActiv 2.0L and 2.5L engines), the firing order is:
- 1-3-4-2
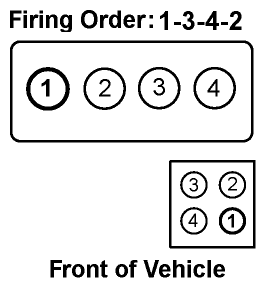
This sequential firing order alternates power strokes between the cylinders, balancing power delivery and minimizing vibrations.
Why Does the Firing Order Matter?
The firing order is critical to the functionality of the Mazda 3’s engine. Here’s why it matters:
Smooth Engine Operation
A proper firing order ensures that power strokes occur at evenly spaced intervals, reducing vibrations and providing a smoother driving experience.
Optimized Power Delivery
The firing order balances the force applied to the crankshaft, maximizing the engine’s ability to deliver consistent power.
Fuel Efficiency
Correct timing ensures complete combustion, which reduces wasted fuel and improves overall efficiency.
Engine Longevity
A balanced firing sequence minimizes wear and tear on the crankshaft, pistons, and other internal components, extending the engine’s life
Understanding the Mazda 3 Engine Layout
The Mazda 3’s inline-4 engine design plays a role in its firing order:
Inline-4 Configuration
The engine features four cylinders arranged in a single line, which simplifies timing and ignition compared to V-shaped engine configurations.
Cylinder Numbering
The cylinders are numbered sequentially from the front of the engine (closest to the timing chain or belt) to the back:
- Cylinder 1: Closest to the timing chain
- Cylinder 4: Farthest from the timing chain
Crankshaft Design
The crankshaft is designed to align with the firing order, ensuring the pistons move up and down in the proper sequence.
Symptoms of Firing Order Issues
When the firing order is disrupted, the engine’s performance can deteriorate significantly. Here are common symptoms:
Engine Misfires
A misfire occurs when one or more cylinders fail to ignite properly, resulting in uneven engine operation and reduced power.
Rough Idling
Incorrect firing can cause the engine to vibrate excessively or idle unevenly.
Loss of Power
An incorrect firing sequence disrupts the engine’s ability to generate smooth and consistent power.
Decreased Fuel Efficiency
Misfires and incomplete combustion waste fuel, leading to lower miles per gallon (MPG).
Excessive Exhaust Smoke
A disrupted firing order may cause unburned fuel to exit through the exhaust, producing excessive smoke.
Check Engine Light
Modern Mazda 3 models will illuminate the check engine light if firing order issues are detected by the onboard diagnostics system.
Diagnosing Firing Order Problems
If you suspect firing order issues in your Mazda 3, follow these diagnostic steps:
Inspect the Ignition System
- Check the spark plugs for fouling, wear, or damage. Replace any that are worn out.
- Test the ignition coils to ensure they are delivering sufficient voltage to the spark plugs.
Verify Cylinder Firing
- Use a timing light to ensure the cylinders are firing in the correct sequence (1-3-4-2).
Perform a Compression Test
- Test each cylinder’s compression using a compression gauge. Low compression can indicate mechanical issues affecting the firing sequence.
Inspect the Timing Chain or Belt
- Check for wear or misalignment in the timing chain or belt, as these can disrupt the engine’s timing and firing order.
Scan for Error Codes
- Connect an OBD-II scanner to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Codes like P030X (where X corresponds to the cylinder number) can pinpoint specific misfire issues.
Fixing Firing Order Problems
Once the root cause of the firing order issue is identified, take these steps to resolve it:
Replace Spark Plugs
- Install new spark plugs that meet Mazda’s specifications. Ensure they are properly gapped to deliver consistent ignition.
Replace Faulty Ignition Coils
- Replace any ignition coils that are damaged or failing. Ignition coils play a crucial role in firing the cylinders in the correct sequence.
Repair the Timing System
- Replace a worn or misaligned timing chain or belt and ensure proper alignment to restore synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft.
Update the Engine Control Unit (ECU)
- If the ECU is causing timing issues, reprogram or replace it as needed.
Address Mechanical Issues
- Repair or replace damaged internal components, such as valves or pistons, that may be affecting compression and firing order.
Preventing Firing Order Issues
Preventive maintenance is the best way to avoid firing order problems and ensure the longevity of your Mazda 3’s engine. Follow these tips:
Regular Tune-Ups
- Schedule periodic inspections of the ignition system, including spark plugs, ignition coils, and timing components.
Use Quality Components
- Invest in high-quality spark plugs and ignition coils to ensure reliable performance.
Monitor Engine Performance
- Pay attention to changes in fuel efficiency, engine noise, or acceleration, as these can indicate underlying problems.
Replace Timing Components as Needed
- Replace the timing chain, belt, or tensioners at the manufacturer’s recommended intervals.
Follow Maintenance Schedules
- Adhere to Mazda’s recommended service intervals to keep your engine in top condition.
Engines with Similar Firing Orders
- 2014 Mazda CX-5 Firing Order
- 2013 Mazda CX-5 Firing Order
- 2018 Mazda CX 5 Firing Order
- 2016 Mazda CX-5 Firing Order
- 2015 Mazda CX-5 Firing Order
FAQs About the Mazda 3 Firing Order
Why is the firing order important?
The firing order ensures balanced power delivery, efficient combustion, and smooth engine operation.
Can I fix firing order problems myself?
Yes, if you have basic engine knowledge. Ensure spark plug connections are correct, and check timing components with proper tools.
What happens if the firing order is incorrect?
An incorrect firing order causes misfires, loss of power, excessive vibrations, and potential damage to the engine’s internal components.
Is the 1-3-4-2 firing order unique to the Mazda 3?
No, this firing order is common among inline-4 engines due to their design and balance requirements.
Conclusion
The Mazda 3 firing order, 1-3-4-2, is a crucial component of its engine’s operation. By ensuring smooth power delivery, efficient combustion, and minimal vibrations, the firing order contributes to the car’s performance and reliability. Understanding the firing order, diagnosing potential issues, and following preventive maintenance practices are essential for keeping your Mazda 3 running smoothly. With proper care, this stylish and efficient compact car will continue to deliver exceptional performance for years to come.

