The Honda Z6 engine, part of the company’s renowned D-series family, is celebrated for its efficiency, reliability, and versatility.
Found in popular models such as the Honda Civic EX and Si from the mid-1990s, this 1.6-liter inline-four engine has become a favorite among enthusiasts for its performance and potential for upgrades.
A critical aspect of maintaining and tuning this engine is understanding its firing order and the sequence in which the engine’s cylinders fire.
In this guide, we’ll explore the Z6 engine’s firing order, its importance, and practical tips for maintenance and troubleshooting. Whether you’re a Honda enthusiast or a curious car owner, this article provides everything you need to know.

Quick Navigation
The Z6 Firing Order
The firing order for the Honda Z6 engine is: 1-3-4-2
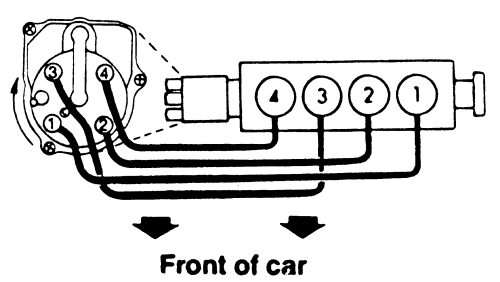
How the Firing Order Works
- Cylinder 1 Fires First: Located at the front of the engine, closest to the timing belt, it initiates the combustion cycle.
- Cylinder 3 Fires Second: Skipping Cylinder 2, the ignition moves to the third cylinder for balanced operation.
- Cylinder 4 Fires Third: The rearmost cylinder ignites, continuing the sequence.
- Cylinder 2 Fires Last: Combustion ends with the second cylinder before the cycle repeats with Cylinder 1.
This pattern alternates firing events across the cylinders, ensuring smooth power delivery and minimizing vibrations.
Why Honda Uses the 1-3-4-2 Firing Order for the Z6
The 1-3-4-2 firing order is carefully chosen to suit the Z6 engine’s design and dynamics. Here’s why it works:
- Crankshaft Design: Matches the crankshaft’s throw arrangement, minimizing mechanical stress.
- Engine Balance: Alternating combustion events reduce vibrations, especially in inline-four configurations.
- Efficiency: Allows enough time for each cylinder’s air-fuel mixture to burn completely.
- Durability: Ensures even wear on the engine’s moving parts, such as the crankshaft and connecting rods.
What Is a Firing Order?
The firing order refers to the sequence in which the cylinders in an internal combustion engine ignite their air-fuel mixture. This controlled combustion drives the pistons, rotates the crankshaft, and generates power. In the Z6’s inline-four configuration, the firing order is critical to ensure smooth and balanced operation.
Why the Firing Order Matters
- Smooth Operation: Ensures balanced power delivery and reduces engine vibrations.
- Efficiency: Optimized timing promotes complete combustion, improving fuel economy.
- Durability: Distributes mechanical stress evenly across the crankshaft and other components.
- Performance: Proper firing order ensures consistent torque and smooth acceleration.
Overview of the Honda Z6 Engine
The Honda Z6 engine is part of the D-series SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engines, with a 16-valve VTEC system. Its compact design and advanced engineering make it a popular choice for both daily driving and performance builds.
Key Features of the Z6 Engine
- Displacement: 1.6 liters.
- Inline-Four Layout: Four cylinders are arranged in a straight line.
- SOHC VTEC Technology: Provides improved airflow and efficiency at higher RPMs.
- Fuel Injection: Electronic fuel injection ensures precise fuel delivery.
- Cylinder Numbering:
- Cylinders are numbered sequentially from left to right (front to back in the engine bay).
- Cylinder 1 is closest to the timing belt, while Cylinder 4 is furthest.
Identifying the Firing Order
To work on or verify the firing order, you need to understand the cylinder layout and ignition system.
Cylinder Numbering
The Z6 engine’s cylinders are numbered sequentially from left to right (when facing the engine):
- Cylinder 1: Closest to the timing belt.
- Cylinder 4: Furthest from the timing belt.
Ignition System
The Honda Z6 engine uses a distributor-based ignition system. A distributor cap and rotor direct spark to the spark plugs in the correct firing sequence.
Symptoms of an Incorrect Firing Order
An incorrect firing order can disrupt engine performance and cause noticeable problems. Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent further damage.
Common Symptoms
- Engine Misfires: Cylinders fail to ignite properly, leading to uneven power delivery.
- Rough Idling: Excessive vibrations or instability at idle due to unbalanced firing.
- Power Loss: Reduced acceleration and sluggish performance.
- Backfiring: Combustion occurs in the intake or exhaust system due to incorrect timing.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Inefficient combustion results in higher fuel usage and emissions.
Diagnosing and Fixing Firing Order Issues
If you suspect a problem with the firing order, follow these steps to diagnose and fix it.
Diagnostic Steps
- Inspect Spark Plug Wires: Verify that each wire is connected to the correct cylinder based on the 1-3-4-2 firing order.
- Check the Distributor Cap: Ensure that the distributor cap is aligned correctly with the rotor.
- Use a Timing Light: Confirm that the ignition timing matches the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Perform a Compression Test: Ensure all cylinders have adequate compression to support proper firing.
Fixing Common Issues
- Reconnect Spark Plug Wires: Route the wires correctly according to the firing order and cylinder numbering.
- Replace Faulty Components: Install new spark plugs, ignition wires, or a distributor cap if they show signs of wear.
- Adjust Timing: Use a timing light and adjust the distributor as necessary.
Preventative Maintenance for Firing Order Reliability
Maintaining the correct firing order is essential for the longevity and performance of your Z6 engine. Follow these preventative tips to avoid issues:
Regular Inspections
- Check spark plugs, ignition wires, and distributor components for wear or damage.
- Inspect timing belts and associated components for proper alignment.
Replace Components as Needed
- Replace spark plugs and ignition wires according to Honda’s maintenance schedule.
- Use high-quality OEM parts to ensure reliability and compatibility.
Monitor Engine Performance
- Pay attention to changes in engine behavior, such as rough idling or power loss.
- Use diagnostic tools to identify and address potential issues early.
FAQs About the Z6 Firing Order
Can I Change the Firing Order?
No, the firing order is determined by the engine’s design and crankshaft configuration. Altering it would require extensive modifications.
What Happens If the Firing Order Is Incorrect?
An incorrect firing order can cause misfires, power loss, backfiring, and potential damage to engine components.
How Can I Verify the Firing Order?
Refer to the engine’s service manual, inspect spark plug wire connections, and use timing tools like a timing light.
Is the Firing Order the Same for All Inline-Four Engines?
While many inline-four engines share the 1-3-4-2 firing order, some variations exist depending on the manufacturer and engine design.
Engines with Similar Firing Orders
- 2010 Honda Odyssey Firing Order
- 2004 Honda Civic Firing Order
- 2001 Honda Civic Firing Order
- 2002 Honda Civic Firing Order
- 2002 Honda Accord Firing Order
Conclusion
The 1-3-4-2 firing order is a crucial element of the Honda Z6 engine’s design, ensuring smooth performance, balanced power delivery, and efficient combustion. Understanding and maintaining this firing order is essential for keeping your Z6 engine running reliably, whether you’re driving a stock Honda Civic or a modified performance build.
By following proper maintenance practices, addressing issues promptly, and using high-quality parts, you can extend the life of your Z6 engine and enjoy its renowned reliability. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, mastering the firing order is a key step in caring for this iconic Honda engine.

