The ROCAM engine, short for Roller Finger Camshaft, is a robust and reliable engine used in several Ford models, including the Fiesta and Bantam. Renowned for its durability and simplicity, the ROCAM engine has become a favorite among car enthusiasts and mechanics.
One critical aspect of its operation is the firing order—the sequence in which its cylinders ignite their air-fuel mixture.
Understanding the ROCAM firing order is essential for maintenance, troubleshooting, and ensuring optimal engine performance. In this guide, we’ll break it all down in a clear and engaging manner.

Quick Navigation
What is the Firing Order for ROCAM engine?
For the Ford ROCAM engine, the firing order is 1-3-4-2.
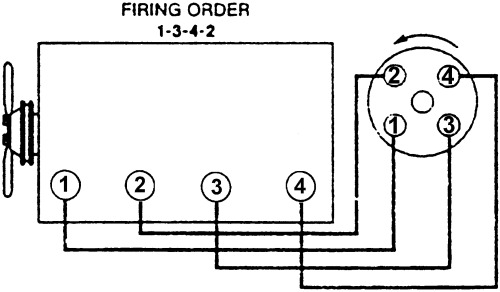
The firing order refers to the sequence in which an engine’s cylinders ignite their air-fuel mixture during operation. This process drives the pistons, rotates the crankshaft, and generates the power needed to move the vehicle.
This sequence ensures that the power strokes are distributed evenly, reducing vibrations and maintaining engine balance.
Why is the Firing Order Important?
The firing order directly affects the engine’s performance and reliability. Here’s why it matters:
Smooth Engine Operation
A balanced firing order minimizes vibrations and ensures the engine runs smoothly, delivering the quiet and reliable operation drivers expect.
Efficient Combustion
The firing order ensures that each cylinder fires at the optimal time, maximizing the combustion process and improving fuel efficiency.
Consistent Power Delivery
The firing order prevents imbalances that could harm the crankshaft by distributing the power strokes evenly throughout the engine’s rotation.
Reduced Wear and Tear
A proper firing sequence reduces stress on internal components, extending the engine’s lifespan and preventing premature wear.
Avoidance of Misfires
The correct firing order ensures that all cylinders fire in sync with the engine’s timing, preventing misfires and power loss.
Understanding the ROCAM Engine Layout
Understanding the layout of the ROCAM engine is important to fully grasp the firing order. This engine typically features an inline-four configuration, meaning all four cylinders are arranged in a straight line.
Cylinder Numbering
In the ROCAM engine:
- Cylinder 1: Closest to the timing belt or accessory drive (front of the engine).
- Cylinder 4: Farthest from the timing belt, near the flywheel.
The numbering progresses sequentially, making it easy to identify each cylinder and understand its position in the firing sequence.
The Firing Order: 1-3-4-2
The 1-3-4-2 firing order is a standard configuration for inline-four engines like the ROCAM. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
Cylinder 1 Fires First
Located at the front of the engine, cylinder 1 begins the power cycle by igniting its air-fuel mixture.
Cylinder 3 Fires Next
The ignition process moves to cylinder 3, located in the middle of the engine.
Cylinder 4 Fires Third
The sequence shifts to cylinder 4, furthest from the timing belt.
Cylinder 2 Fires Last
Finally, cylinder 2 fires, completing the cycle before it repeats.
This alternating pattern balances the power strokes across the crankshaft, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
Components Supporting the Firing Order
Several critical components work together to execute the firing order in the ROCAM engine. Each plays a vital role in maintaining proper timing and combustion:
Crankshaft
The crankshaft converts the pistons’ up-and-down motion into rotational energy, aligning with the firing sequence to deliver power to the drivetrain.
Camshaft
The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves, ensuring precise timing for each cylinder.
Ignition Coil Pack
The ignition coil pack generates the high-voltage electricity needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture. The ROCAM engine delivers this energy in the correct firing order.
Spark Plugs
Spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture in each cylinder, creating the power strokes that drive the engine.
Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The ECU manages ignition timing and fuel delivery, ensuring the firing order is executed accurately and efficiently.
Symptoms of Firing Order Issues
If the firing order is disrupted or incorrect, the ROCAM engine will exhibit noticeable symptoms. Recognizing these early can help prevent significant engine damage:
Engine Misfires
Cylinders firing out of sequence can cause misfires, resulting in rough operation and reduced power.
Rough Idling
The engine may vibrate excessively or stall during idle if the firing order is incorrect.
Loss of Power
An imbalanced firing sequence reduces the engine’s efficiency, leading to sluggish acceleration and weak performance.
Knocking or Backfiring
Premature combustion caused by incorrect timing can produce knocking sounds or backfires.
Increased Fuel Consumption
A misaligned firing order forces the engine to work harder, burning more fuel than necessary.
Diagnosing and Correcting Firing Order Issues
If you suspect a problem with the firing order in your ROCAM engine, follow these steps to diagnose and resolve it:
Step 1: Inspect the Ignition System
- Check the ignition coil pack and spark plug wires to ensure they are connected to the correct cylinders according to the 1-3-4-2 firing order.
- Replace any damaged or worn components.
Step 2: Check Spark Plug Health
- Remove and inspect the spark plugs for signs of wear, fouling, or damage. Replace them if necessary.
Step 3: Verify Engine Timing
- Use a timing light to check the ignition timing. Ensure it aligns with the manufacturer’s specifications.
Step 4: Consult the Service Manual
- Refer to the Ford service manual for detailed diagrams and instructions related to the ROCAM engine’s ignition system.
Step 5: Test the Engine
- After making adjustments, start the engine and monitor its performance. Look for smooth idling, balanced power, and reduced vibrations.
Maintenance Tips to Preserve the Firing Order
Regular maintenance is essential to keep the firing order intact and ensure that the engine is performing at its best. Here are some tips:
Replace Spark Plugs Periodically
Worn or fouled spark plugs can disrupt ignition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended replacement intervals.
Inspect Ignition Components Regularly
Check ignition wires, coil packs, and other components for signs of wear or corrosion. Replace any faulty parts immediately.
Clean the Fuel System
Maintain the fuel injectors and lines to ensure efficient combustion in all cylinders.
Monitor the ECU
Use diagnostic tools to check for error codes or misfire indications and address any issues promptly.
Verify Timing During Routine Maintenance
Use a timing light to ensure the ignition timing remains aligned with the firing order.
Common Misconceptions About Firing Order
“All Inline-Four Engines Have the Same Firing Order”
While 1-3-4-2 is common, some inline-four engines use different firing orders depending on their design.
“You Can Adjust the Firing Order for Performance”
Altering the firing order without redesigning the engine can cause severe mechanical issues and reduce efficiency.
“Firing Order Doesn’t Affect Longevity”
An incorrect firing order increases stress on the engine, leading to premature wear and damage.
Engines with Similar Firing Orders
- 429 Ford Firing Order
- 2011 Ford Escape Firing Order
- Ford F150 Firing Order for 4.2
- 2007 Ford Escape Firing Order
- 2005 Ford Escape Firing Order
Conclusion
The firing order of the Ford ROCAM engine, 1-3-4-2, is fundamental to its smooth operation, efficiency, and longevity. By understanding this sequence and maintaining the components that support it, you can ensure your engine delivers reliable performance for years to come. Whether you’re troubleshooting an issue or performing routine maintenance, knowledge of the firing order is a vital tool in keeping your ROCAM engine running at its best.
With regular care and attention, your ROCAM engine will continue to provide the dependable performance and durability that have made it a favorite among drivers and mechanics alike.

