You’re in for a “crash course” on Iowa’s laws. You’ll need to know the basics of booster seat regulations, and it’s essential to understand the specifics to guarantee child safety.
Quick Navigation
Key Takeaways
- Children must use booster seats until age 6.
- No maximum weight limit is specified for booster seats.
- Proper fit is essential for booster seats.
- Children must ride in the back seat.
- Iowa Code 321.446 outlines car seat requirements.
Understanding Iowa Booster Seat Law
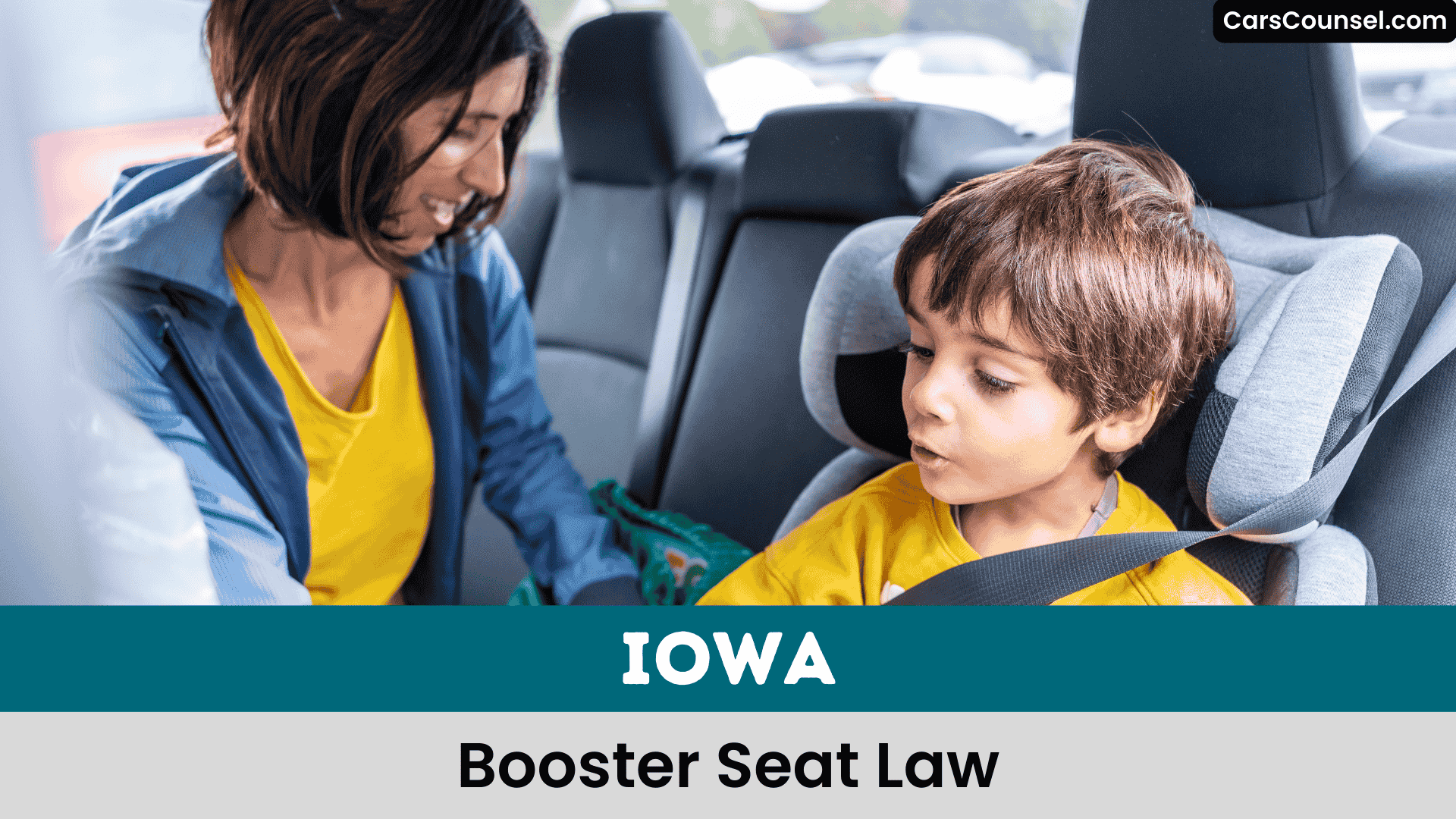
When you’re driving with kids in Iowa, it’s vital to understand the state’s booster seat law.
You must guarantee child passenger safety by using booster seats until they fit properly. Iowa’s Car Seat Laws require booster seats until at least age 6, with no maximum weight limit specified.
Proper use is essential, so check that kids fit properly, with knees bending and feet touching the floor, to ascertain safe travel.
Types of Car Seats and Child Restraints
You’ll find two primary types of car seats and child restraints that serve distinct purposes: booster seats and other restraint systems.
- Booster seats
- Forward-facing car seat’s
- Child restraint
- Maximum weight or height
- Child safety is key, consult a law firm.
Car Seat Calculator Basics
Having considered the types of car seats and child restraints, it’s time to focus on the tools that help you choose the right one.
You can use a car seat calculator to determine the best booster seat based on your child’s weight and height. A child passenger safety technician or car seat manufacturer can guide you.
Check the expiration date and verify your child sits safely, following the calculator’s recommendations for ideal child safety.
Heatstroke Prevention Measures
As heatstroke can occur rapidly, even on mild days, it’s essential to take preventive measures to guarantee your child’s safety in vehicles.
- Check the back seat before locking
- Keep your vehicle secured
- Don’t leave a child alone
- Call 911 if needed
- Stay informed about routine changes
Vehicle-Related Hazards to Children
Vehicle-related hazards pose a significant threat to children’s safety, and it’s crucial that parents and caregivers take proactive steps to mitigate these risks.
You must guarantee a proper seat belt fits to prevent injury in a car accident.
The Traffic Safety Bureau warns that children under the age of 15 are vulnerable, so prioritize your child’s safety to avoid tragic outcomes.
Child Passenger Safety in Iowa
When you’re driving with kids in Iowa, it’s essential you understand the state’s child passenger safety laws to secure their safety on the road.
You must ensure proper restraint, including a booster seat or seat belt, as per Iowa law.
Key considerations include:
- Using a booster seat
- Riding in the back seat
- Wearing a seat belt
- Following Iowa law
- Ensuring proper fit
Safety Guidelines for Children
You’ll want to focus on safety guidelines for children to guarantee they’re properly secured in your vehicle.
| Age and Weight | Booster Seat |
|---|---|
| 6-17 years | required |
| varies | seat belt |
| under 6 | car seat |
| over 80 lbs | may not need |
| 4’9″ or taller | seat belt only |
Iowa Car Seat Laws Overview
Iowa’s car seat laws, as outlined in Iowa Code 321.446, require children under 1 year and weighing less than 20 pounds to use a rear-facing car seat, while children under 6 years and over 20 pounds must use either front-facing car seats or booster seats.
You must:
- Use a rear-facing car seat
- Transition to a booster seat
- Follow the three-step test
- Adhere to maximum weight
- Use seat belts or child restraint devices
Child Restraint Device Laws
Child restraint device laws in Iowa build on the state’s car seat laws, which require children to use specific types of seats based on their age and weight. You must follow the manufacturer’s instructions for child restraint devices.
| Age | Requirement |
|---|---|
| 1-5 | child restraint device |
| 6-17 | booster or seat belt |
| under 1 | rear-facing seat |
| 8-12 | pass seat belt test |
| all | follow seat belt guidelines |
Proper Use of Booster Seats
As children outgrow their forward-facing car seats, they should transition to a booster seat, which helps position the vehicle’s seat belt correctly across their body for maximum safety.
Transition to a booster seat for proper seat belt positioning and maximum safety as children outgrow forward-facing car seats.
You must guarantee they’re properly restrained.
- Check the lap belt
- Adjust the shoulder belt
- Verify the maximum weight
- Confirm children must use it
- Monitor their growth
Child Safety Laws in Iowa
When you’re driving in Iowa, you must comply with the state’s child safety laws to guarantee your kids are properly secured in your vehicle.
You’ll need a booster seat until they fit the vehicle seat. Follow Iowa Code 321.446 for proper installation.
Kids must ride in the back seat and use a booster seat or seat belt, ensuring they’re safely secured in the vehicle seat.
Enhancing Child Safety on the Road
You’ll improve child safety on the road by following Iowa’s booster seat law, which requires children to use a booster seat or seat belt that fits properly.
As you review the road rules, you’ll notice that booster seats play an essential role in reducing the risk of injury in the event of a crash.
You can guarantee your child’s safety by selecting the correct type of booster seat, such as a high back or low back booster, and verifying they can pass the five-step test to transition out of it.
Child Safety
Child safety on the road is a top priority, and it’s essential that you take the necessary precautions to secure your child’s well-being while driving.
You must use a booster seat, confirming the lap and shoulder belt fit correctly.
- Use a booster seat
- Ride in the back seat
- Wear age-appropriate restraints
- Use the vehicle’s seat belt
- Verify proper fit
Road Rules
The use of front, and back of the vehicle and the proper use of restraints are a must to follow the law on the road. You’ll reduce injury risk in a car accident with proper installation of booster seats.
| Booster Seats | Iowa Law |
|---|---|
| Ages 6-18 | Required |
| High back | Mandatory |
| Low back | Allowed |
| Proper use | Reduces injury |
| Installation | Essential |
Booster Seats
Boosting child safety on the road involves more than just following general road rules.
You must guarantee your child fit in a booster seat. In Iowa, this is law.
Key points include:
- Using a booster seat reduces serious injury risk
- Lap belt on upper thighs
- Shoulder belt across shoulder and chest
- High back booster for vehicles without headrests
- Compliance with Iowa law
State-by-State Booster Seat Laws: Age/Weight Requirements, Rules & Penalties
| Alabama | Alabama requires children age 5 and under to ride in a child safety seat; booster seats are mandated for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age/weight limits are met. Penalties include fines for noncompliance. |
| Alaska | Alaska’s law mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height thresholds. Failure to comply can result in citations and fines. |
| Arizona | Arizona requires children under age 5 in appropriate child restraints; boosters are required until children reach height/weight guidelines. Violations may lead to fines. |
| Arkansas | Arkansas requires booster seats for children ages 4–8 who outgrow forward-facing seats until they meet height/weight requirements; noncompliance can lead to penalties. |
| California | California mandates booster seats for children under age 8 unless they are 4’9″ tall. Violations result in fines and may increase insurance costs. |
| Colorado | Colorado law requires boosters for children over forward-facing limits through age 8 or until height/weight thresholds are met. Fines apply for nonuse. |
| Connecticut | Connecticut requires booster seats for children under age 8 who have outgrown forward-facing seats. Penalties include fines for noncompliance. |
| Delaware | Delaware mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits up to age 8; infractions can lead to monetary penalties. |
| Florida | Florida requires children under age 6 to be in an appropriate child restraint; boosters are recommended until height/weight limits are met. Violations can result in fines. |
| Georgia | Georgia law requires boosters for children ages 4–7 who exceed forward-facing seat limits until they reach height/weight thresholds. Penalties include fines. |
| Hawaii | Hawaii mandates booster seats for children who have outgrown forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height/weight requirements; fines apply for nonuse. |
| Idaho | Idaho requires booster seats for children after forward-facing stage through age 7 or until height/weight thresholds are met. Noncompliance carries fines. |
| Illinois | Illinois law requires booster seats for children under age 8 unless they exceed height/weight limits; violations result in fines. |
| Indiana | Indiana mandates boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing seats through age 7 or until meeting height/weight standards; penalties include fines. |
| Kansas | Kansas mandates booster seats for children who have outgrown forward-facing seats through age 8 or until height/weight limits are met; violations carry fines. |
| Kentucky | Kentucky law requires boosters for children over forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight criteria; infractions result in fines. |
| Louisiana | Louisiana mandates booster seats for children after the forward-facing stage up to age 8 or until proper height/weight is reached; fines apply. |
| Maine | Maine requires booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; noncompliance may lead to fines. |
| Maryland | Maryland law mandates boosters for children beyond forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight thresholds; penalties include fines. |
| Massachusetts | Massachusetts requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing stages until age 8 or height/weight limits; fines apply for violations. |
| Michigan | Michigan mandates booster seats for children after forward-facing stage through age 8 or until height/weight requirements are met; fines may be assessed. |
| Minnesota | Minnesota requires boosters for children who exceed forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; noncompliance results in fines. |
| Mississippi | Mississippi mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or until proper height/weight; violations carry fines. |
| Missouri | Missouri’s booster seat law requires usage for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 7 or height/weight thresholds; fines may apply. |
| Montana | Montana requires booster seats for children after forward-facing limits until age 7 or height/weight benchmarks; fines for noncompliance. |
| Nebraska | Nebraska mandates booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats through age 8 or until height/weight limits are met; penalties include fines. |
| Nevada | Nevada’s law requires boosters for children after forward-facing limits until age 6 or height/weight criteria are met; fines may be imposed. |
| New Hampshire | New Hampshire requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits up to age 7 or until height/weight thresholds apply; fines for violations. |
| New Jersey | New Jersey mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing stages until age 8 or height/weight limits; noncompliance results in fines. |
| New Mexico | New Mexico requires booster seats after forward-facing limits through age 7 or height/weight thresholds; violations may lead to fines. |
| New York | New York’s booster seat law requires usage until age 8 or until height/weight limits are met. Penalties include fines and possible points. |
| North Carolina | North Carolina mandates booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines apply. |
| North Dakota | North Dakota requires booster seats after forward-facing stage through age 7 or until height/weight thresholds; penalties include fines. |
| Ohio | Ohio mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; fines may be assessed. |
| Oklahoma | Oklahoma requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight benchmarks; fines apply. |
| Oregon | Oregon’s booster seat law mandates usage for children after forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight requirements; penalties include fines. |
| Pennsylvania | Pennsylvania requires boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight limits; fines apply for noncompliance. |
| Rhode Island | Rhode Island mandates boosters until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met. Violations may result in fines. |
| South Carolina | South Carolina requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight benchmarks; fines apply. |
| South Dakota | South Dakota mandates boosters for children after forward-facing stage until age 7 or height/weight limits; penalties include fines. |
| Tennessee | Tennessee requires booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines may be imposed. |
| Texas | Texas mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight thresholds; violations result in fines. |
| Utah | Utah’s booster seat law requires usage until age 8 or until height/weight requirements are met; fines apply for violations. |
| Vermont | Vermont requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing seat limits until age 8 or height/weight benchmarks. Noncompliance carries fines and possible points. |
| Virginia | Virginia mandates booster seats until age 8 or until height/weight criteria; violations may lead to fines and points. |
| Washington | Washington requires boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height/weight limits; fines can be assessed. |
| West Virginia | West Virginia mandates booster seats until age 8 or height/weight thresholds are met; penalties include fines. |
| Wisconsin | Wisconsin requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines may apply. |
| Wyoming | Wyoming’s booster seat law mandates usage for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight limits; noncompliance results in fines. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Requirements for a Booster Seat in Iowa?
You must follow booster seat regulations, using child safety seats, adhering to car seat guidelines, and Iowa traffic laws, ensuring proper installation methods for vehicle safety standards compliance always.
At What Height and Weight Can You Get Out of a Booster Seat?
“Measure twice, cut once” applies to booster seat guidelines, you’ll exit when meeting height weight requirements, typically 4’9″ tall, and proper seatbelt usage is guaranteed, following child safety seats and car seat regulations.
Can a 4 Year Old Use a Backless Booster Seat?
You can use a backless booster seat at 4 years old if meeting manufacturer’s height and weight requirements, ensuring backless booster safety and complying with age requirements for booster seat regulations.
Does a 10 Year Old Need to Sit in a Booster Seat?
You determine if a 10-year-old needs a booster seat by checking they meet safety regulations, considering booster seat age, and following car seat guidelines and seat belt laws.
Conclusion
You’ve learned about Iowa’s booster seat law, but will you use this knowledge to guarantee your child’s safety? You must follow the regulations to prevent accidents. Properly using a booster seat is essential, so you can’t afford to overlook the guidelines. By doing so, you’ll significantly reduce the risk of injury or death, making Iowa’s roads safer for children.

