Like a seatbelt clicking into place, Montana’s new law secures a safer future. You’ll need to know the specifics, as it affects you.
Quick Navigation
Key Takeaways
- Montana’s booster seat law starts October 1, 2025.
- Applies to children aged 4 to 8 years old.
- Requires forward-facing car seat or booster seat.
- Aims to improve child passenger safety standards.
- Aligns with federal child safety regulations.
Overview of Montana Booster Seat Law
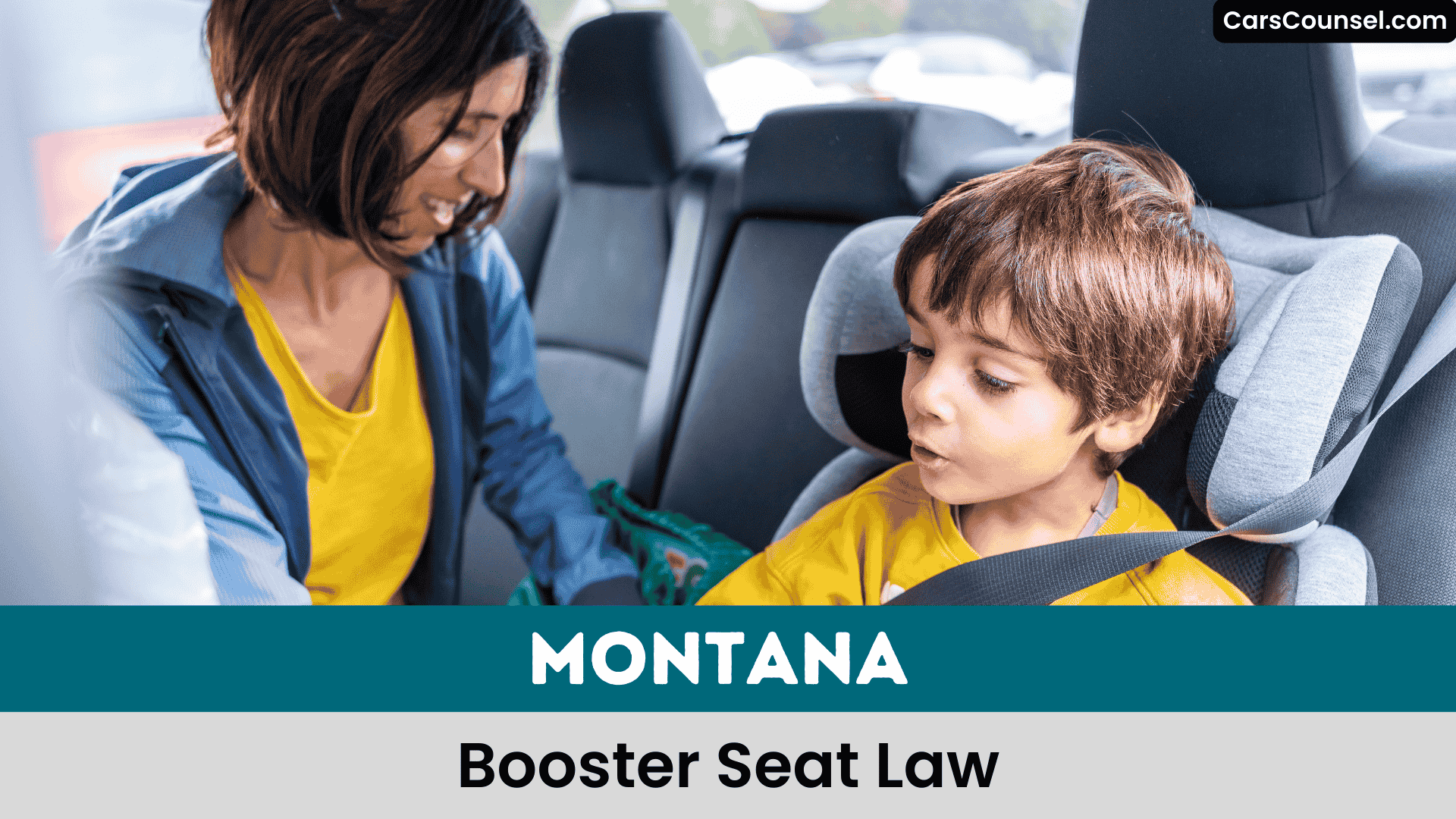
As you review Montana’s child passenger safety regulations, you’ll find that the state’s new booster seat law, which takes effect on October 1, 2025, requires children aged 4 to 8 to use a forward-facing car seat with an internal harness or a booster seat based on their size.
Montana’s new booster seat law improves child passenger safety by promoting proper use of car seats and booster seats, reducing injury risks with booster seats, and aligning with federal standards.
Changes to Child Restraint Requirements
Montana’s updated child passenger safety regulations introduce significant changes to child restraint requirements.
You’ll need to use a rear-facing car seat for children under 2, or a forward-facing car seat or booster seats for those aged 4-8.
These child car seat laws improve child passenger protection, aligning with national standards.
Guidelines for Aging Out of Booster Seats
When do you know it’s time for your child to stop using a booster seat?
You’ll know when they’re about 4 feet 9 inches tall or 9 years old.
Make sure they’re properly restrained, with the seat belt fitting correctly.
Booster seats improve child safety by 59%.
Law enforcement verifies compliance, so check your child’s fit regularly to determine when they can safely transition out of booster seats.
Importance of Proper Car Seat Installation
Proper car seat installation is crucial because nearly half of all car seats are installed incorrectly, which can significantly compromise a child’s safety in a crash.
You must guarantee seats and booster seats are properly restrained. When car seats are installed correctly, they provide ideal child safety, reducing fatal injury risks.
Regular checkups can help verify that your child is properly restrained, assuring their safety while riding in vehicles with correctly installed car seats.
Impact on Child Passenger Safety
As you consider the safety of your child while riding in a vehicle, it’s essential to understand the impact of the new booster seat law on child passenger safety.
The law requires a booster or car seat for children aged 4-8, reducing injury risk by 59%. This law improves child safety, aligning Montana’s standards with federal guidelines, and promotes safe progression to adult seat belts, ultimately protecting your child with a properly used booster seat.
Community Resources for Car Seat Safety
You can access community resources that provide car seat checks, which help you verify the correct installation of your child’s car seat.
Local organizations, such as fire departments and public health departments, offer free resources, including car seat checkup events and educational materials, to support you in keeping your child safe.
Car Seat Checks
Many community resources across Montana offer certified technicians for car seat checks, ensuring that seats are installed and used correctly. You can get your car seat checked by technicians.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Bozeman Fire | Car seat checks |
| Great Falls Fire | Installation guidance |
| Local Law | Education on safety |
Free Resources
The state of Montana provides numerous free resources to support community car seat safety.
You can access free car seats and installation assistance through community programs. These initiatives promote child passenger safety, offering guidance on proper car seat usage.
Community programs and public health departments provide resources, connecting you with certified technicians for tailored support, ensuring you’re equipped to keep your child safe on the road.
Car Seat Usage Guidelines by Age
You’ll need to contemplate the age of your child when choosing a car seat, as Montana’s booster seat law outlines specific guidelines for different age groups.
You must guarantee that children under 2 years old are secured in a rear-facing car seat, while those between 2 and 4 years old can use either a rear-facing or forward-facing car seat with an internal harness.
As you determine the appropriate car seat for your child, you’ll need to contemplate both the age guidelines and the corresponding seat requirements, such as moving to a booster seat or standard adult seat belt at the appropriate age or size.
Age Guidelines
Eight out of ten children don’t use car seats correctly, so it’s crucial to follow Montana’s car seat usage guidelines by age.
You must guarantee your child is properly restrained. The new car seat law outlines specific age guidelines for car seat usage.
Children under 2 must use rear-facing seats, while those aged 2-4 can use rear or forward-facing seats.
You’ll need to adjust car seat usage as your child grows, following Montana’s age guidelines to keep them safe.
Seat Requirements
Most children don’t use car seats correctly, so it’s essential to follow Montana’s car seat usage guidelines by age.
You’ll need a rear-facing car seat for kids under 2, then a forward-facing seat or booster seat as they grow.
For kids 4-8, use a forward-facing seat or booster seat.
Once they’re 9 or outgrow their booster, they can use an adult seat belt, ensuring a safe transition from car seats to a seat belt.
Safety Statistics and Impact of New Law
Numerous safety statistics underscore the importance of the new Montana booster seat law, which aims to reduce child fatalities in car crashes – a stark reality that claims about three young lives per day in the U.S. You’ll see benefits for children aged 4-8 using a booster seat.
| Safety Benefit | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Reduced injury risk | 59% |
| Proper usage | 71% |
| Fatality rate | exceeds U.S. average |
Legislative Process and Advocacy
As you examine the legislative process behind Montana’s updated child car seat laws, you’ll find that House Bill 586, sponsored by Representative Marc Lee, played an essential role in shaping the new regulations.
Key aspects of the legislation and advocacy for child safety include:
Key aspects include bipartisan support and car seat safety enhancements.
- Bipartisan support
- Car seat manufacturer collaboration
- Federal safety standard alignment, enhancing car seat safety.
Common Installation Issues and Solutions
You’ll find that understanding the legislative process behind Montana’s updated child car seat laws is just the first step in guaranteeing your child’s safety while traveling.
You’ll need help with car seat installation to get it secured correctly. Incorrect installation is common, so it’s essential to follow manuals and make certain the seat doesn’t move more than one inch side to side, to keep your child safe.
Available Assistance and Resources for Car Seat Safety
You can access free resources, such as the Safe Seat for Baby program, which provides car seats and installation guidance to communities in need.
Local fire departments, like the Bozeman Fire Department, also host car seat checkup events to verify you’re using your car seat correctly, and you can get assistance from certified professionals.
You’ll find safety checks and other resources through organizations like Great Falls Fire Rescue and the LIFTS Online Resource Guide, which connect you with certified Child Passenger Safety Technicians for installation help.
Free Resources
Several organizations provide free resources to help families verify their children’s car seats are installed correctly.
You can access
- installation assistance
- car seat safety guides
- community support.
These free resources improve car seat safety, providing you with the tools to secure your child’s safety while traveling.
Safety Checks
As families work to confirm their children’s car seats are installed correctly, numerous community resources across Montana are available to provide assistance.
You can get safety checks and installation assistance to verify compliance with the booster seat law. Local resources offer free car seat checks, and certified technicians provide education on proper installation, helping you make informed decisions about your child’s car seat safety.
State-by-State Booster Seat Laws: Age/Weight Requirements, Rules & Penalties
| Alabama | Alabama requires children age 5 and under to ride in a child safety seat; booster seats are mandated for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age/weight limits are met. Penalties include fines for noncompliance. |
| Alaska | Alaska’s law mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height thresholds. Failure to comply can result in citations and fines. |
| Arizona | Arizona requires children under age 5 in appropriate child restraints; boosters are required until children reach height/weight guidelines. Violations may lead to fines. |
| Arkansas | Arkansas requires booster seats for children ages 4–8 who outgrow forward-facing seats until they meet height/weight requirements; noncompliance can lead to penalties. |
| California | California mandates booster seats for children under age 8 unless they are 4’9″ tall. Violations result in fines and may increase insurance costs. |
| Colorado | Colorado law requires boosters for children over forward-facing limits through age 8 or until height/weight thresholds are met. Fines apply for nonuse. |
| Connecticut | Connecticut requires booster seats for children under age 8 who have outgrown forward-facing seats. Penalties include fines for noncompliance. |
| Delaware | Delaware mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits up to age 8; infractions can lead to monetary penalties. |
| Florida | Florida requires children under age 6 to be in an appropriate child restraint; boosters are recommended until height/weight limits are met. Violations can result in fines. |
| Georgia | Georgia law requires boosters for children ages 4–7 who exceed forward-facing seat limits until they reach height/weight thresholds. Penalties include fines. |
| Hawaii | Hawaii mandates booster seats for children who have outgrown forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height/weight requirements; fines apply for nonuse. |
| Idaho | Idaho requires booster seats for children after forward-facing stage through age 7 or until height/weight thresholds are met. Noncompliance carries fines. |
| Illinois | Illinois law requires booster seats for children under age 8 unless they exceed height/weight limits; violations result in fines. |
| Indiana | Indiana mandates boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing seats through age 7 or until meeting height/weight standards; penalties include fines. |
| Iowa | Iowa requires booster seats for children ages 4–7 who exceed forward-facing stage until they reach height/weight limits; fines may be imposed. |
| Kansas | Kansas mandates booster seats for children who have outgrown forward-facing seats through age 8 or until height/weight limits are met; violations carry fines. |
| Kentucky | Kentucky law requires boosters for children over forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight criteria; infractions result in fines. |
| Louisiana | Louisiana mandates booster seats for children after the forward-facing stage up to age 8 or until proper height/weight is reached; fines apply. |
| Maine | Maine requires booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; noncompliance may lead to fines. |
| Maryland | Maryland law mandates boosters for children beyond forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight thresholds; penalties include fines. |
| Massachusetts | Massachusetts requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing stages until age 8 or height/weight limits; fines apply for violations. |
| Michigan | Michigan mandates booster seats for children after forward-facing stage through age 8 or until height/weight requirements are met; fines may be assessed. |
| Minnesota | Minnesota requires boosters for children who exceed forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; noncompliance results in fines. |
| Mississippi | Mississippi mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or until proper height/weight; violations carry fines. |
| Missouri | Missouri’s booster seat law requires usage for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 7 or height/weight thresholds; fines may apply. |
| Nebraska | Nebraska mandates booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats through age 8 or until height/weight limits are met; penalties include fines. |
| Nevada | Nevada’s law requires boosters for children after forward-facing limits until age 6 or height/weight criteria are met; fines may be imposed. |
| New Hampshire | New Hampshire requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits up to age 7 or until height/weight thresholds apply; fines for violations. |
| New Jersey | New Jersey mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing stages until age 8 or height/weight limits; noncompliance results in fines. |
| New Mexico | New Mexico requires booster seats after forward-facing limits through age 7 or height/weight thresholds; violations may lead to fines. |
| New York | New York’s booster seat law requires usage until age 8 or until height/weight limits are met. Penalties include fines and possible points. |
| North Carolina | North Carolina mandates booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines apply. |
| North Dakota | North Dakota requires booster seats after forward-facing stage through age 7 or until height/weight thresholds; penalties include fines. |
| Ohio | Ohio mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; fines may be assessed. |
| Oklahoma | Oklahoma requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight benchmarks; fines apply. |
| Oregon | Oregon’s booster seat law mandates usage for children after forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight requirements; penalties include fines. |
| Pennsylvania | Pennsylvania requires boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight limits; fines apply for noncompliance. |
| Rhode Island | Rhode Island mandates boosters until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met. Violations may result in fines. |
| South Carolina | South Carolina requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight benchmarks; fines apply. |
| South Dakota | South Dakota mandates boosters for children after forward-facing stage until age 7 or height/weight limits; penalties include fines. |
| Tennessee | Tennessee requires booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines may be imposed. |
| Texas | Texas mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight thresholds; violations result in fines. |
| Utah | Utah’s booster seat law requires usage until age 8 or until height/weight requirements are met; fines apply for violations. |
| Vermont | Vermont requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing seat limits until age 8 or height/weight benchmarks. Noncompliance carries fines and possible points. |
| Virginia | Virginia mandates booster seats until age 8 or until height/weight criteria; violations may lead to fines and points. |
| Washington | Washington requires boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height/weight limits; fines can be assessed. |
| West Virginia | West Virginia mandates booster seats until age 8 or height/weight thresholds are met; penalties include fines. |
| Wisconsin | Wisconsin requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines may apply. |
| Wyoming | Wyoming’s booster seat law mandates usage for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight limits; noncompliance results in fines. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Booster Seat Requirements in Montana?
You must follow booster seat regulations, safety guidelines, and installation tips to minimize common misconceptions, ensuring proper use reduces injury risks for children in Montana.
What Age and Weight Can a Child Get Out of a Booster Seat?
You’re a million times safer knowing a child can exit a booster seat around age 9, following booster seat safety and car seat guidelines, adhering to child passenger laws for ideal protection.
Does My 7 Year Old Still Need a Booster?
You’ll determine if your 7-year-old still needs a booster by checking age, height, and weight requirements, ensuring booster seat safety and adherence to child passenger laws and seatbelt guidelines.
When Can I Switch My Kid Into a Booster Seat?
You can switch your kid to a booster seat when they reach 40 pounds or outgrow their child car seats, following transition guidelines for booster seat safety and vehicle seat belts.
Conclusion
You’ll find the Montana Booster Seat Law improves child safety, with statistics showing that booster seats reduce injury risk by 45%. By following the law, you’re contributing to a significant decrease in child fatalities, making Montana’s roads safer for all. This new law is an important step in protecting children, and it’s essential you understand its requirements.

