Ironically, you’re likely unaware of Nevada’s booster seat law. You’ll need to know it to guarantee child safety.
Quick Navigation
Key Takeaways
- Nevada requires booster seats for children under 57 inches tall.
- Booster seats are needed until children weigh at least 60 pounds.
- Children under 6 years old need approved car seats or boosters.
- Booster seats are mandatory after outgrowing forward-facing seats.
- Nevada law enforces booster seat use for child safety.
Overview of Nevada Car Seat Laws
When you’re driving in Nevada with kids, it’s essential you understand the state’s car seat laws to guarantee their safety.
Nevada car seat laws require children to use child restraint systems, including forward-facing car seats and booster seats, based on age and weight limits.
The Nevada Department of Transportation enforces these laws, ensuring kids use approved child safety seats, including booster seats, to minimize risks.
Required Car Seats for Small Children
You’ll need to understand the specific car seat rules in Nevada to guarantee your child’s safety while traveling.
As you research the requirements, you’ll find that car seat regulations are based on the child’s age, weight, and height, and it’s essential to choose a seat that complies with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
You must select a car seat that meets these standards and follows the recommended seat requirements to provide the best possible protection for your child.
Car Seat Rules
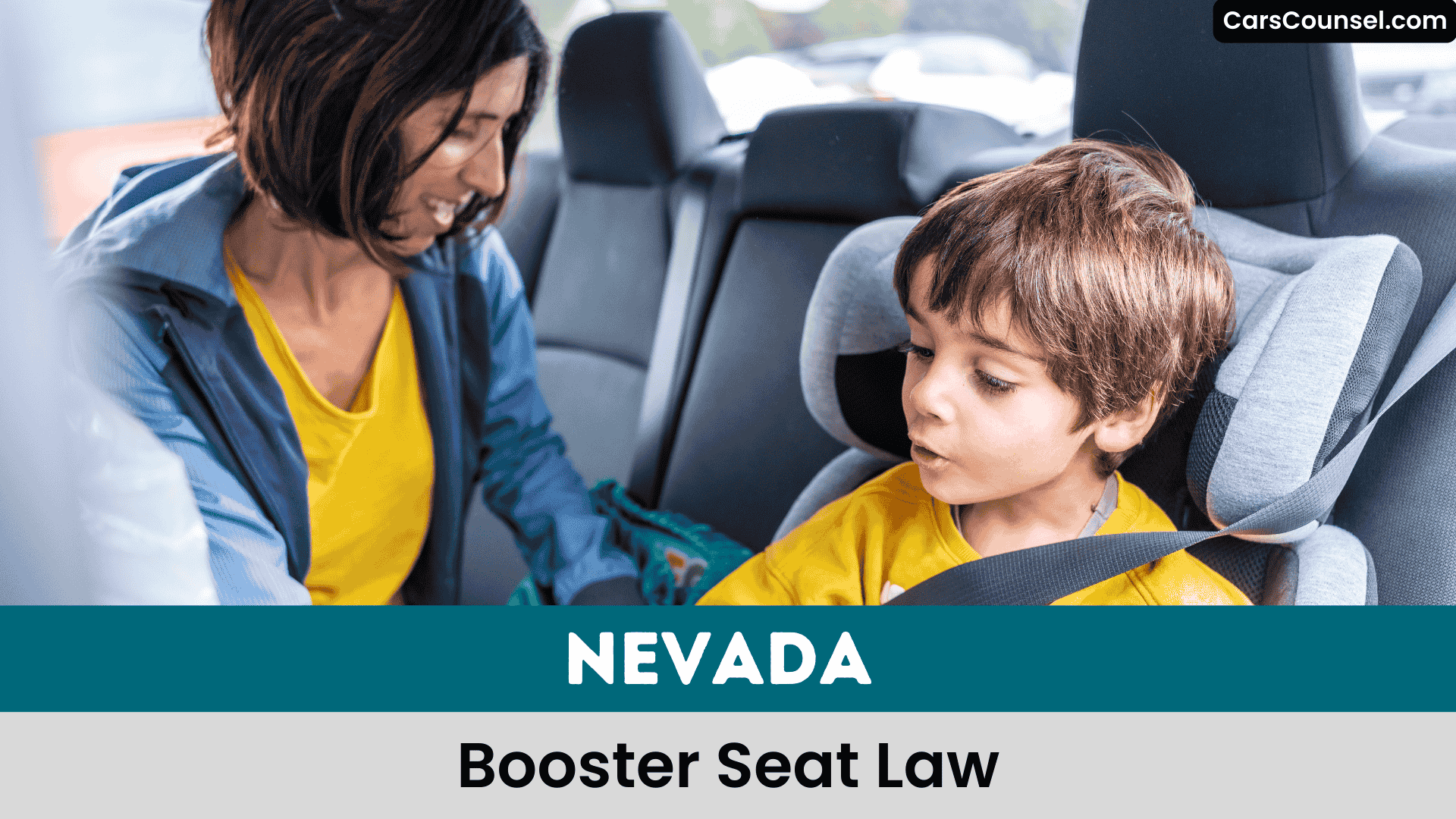
As Nevada’s car seat laws dictate, children under 6 years old and weighing less than 60 pounds must use an approved car seat or booster seat that complies with Department of Transportation standards.
You must use a rear-facing seat for children under 2, then transition to a forward-facing car seat, and eventually a booster seat, ensuring proper use and adherence to weight limits, promoting child safety in the back seat.
Child Safety
Child safety is a top priority in Nevada, and the state’s laws dictate that children under 6 years old and less than 57 inches tall must use a booster seat or car seat that meets federal safety standards.
You must guarantee the seat belt fits properly, following Nevada law and booster seat requirements for Child Passenger Safety, using an appropriate child restraint to protect children under 6 years old.
Seat Requirements
Six years old is the threshold for booster seat requirements in Nevada, where kids under this age and less than 57 inches tall or 60 pounds must use an approved car seat or booster seat.
You must comply with Nevada law, ensuring children under 6 years meet car seat requirements, including weight limits, for safety during travel, using a Department of Transportation-approved car seat or booster seats.
Booster Seat Weight Requirements
You need to reflect on the weight limits for booster seats, which dictate that children must use them until they weigh at least 60 pounds or reach a certain age.
As you assess booster seat requirements, you’ll find that the law specifies a transition to a booster seat after a child outgrows their forward-facing car seat, typically around 40 pounds.
You must also be aware of the age restrictions, which allow children to stop using a booster seat when they’re at least 6 years old, or when they meet certain height and seat belt fit criteria.
Weight Limits
Nevada’s booster seat law sets specific weight limits for kids’ safety on the road.
You must guarantee children use a booster seat until they’re at least 6 years old or weigh 60 pounds.
Nevada law requires a child restraint system for children under 57 inches tall.
Failure to comply can result in fines.
You’ll avoid fines by following the law, keeping your children safe with a properly fitted booster seat, adhering to Nevada’s weight limits for children’s safety.
Seat Requirements
Because children grow at different rates, it’s essential to contemplate their weight and height when determining if a booster seat is required.
You must verify your child’s booster seat meets the manufacturer’s requirements.
Children under 13 years should use booster seats in the back seat for maximum protection.
Booster seats raise them so seat belts fit properly, providing maximum protection.
They’re necessary after outgrowing a forward-facing car seat until they fit properly in seat belts.
Age Restrictions
Seven states, including Nevada, have laws that require children to use a booster seat based on their age, weight, or height.
You must guarantee children aged 4-12 use a booster seat until they weigh 60 pounds or reach 57 inches.
Nevada law prioritizes safety, facilitating a smooth transition to seat belts when children reach the correct height and weight, typically between 8-12 years old.
Installing the Car Seat Correctly
When installing a car seat, you must follow the guidelines set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer to guarantee the seat is properly secured.
| Car Seat | Age Weight Height | Safety Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Booster | 4-12 yrs | Back seat |
| Child | 0-4 yrs | Correctly every time |
| Infant | 0-1 yr | Nevada law requires |
| Convertible | 0-7 yrs | Tight installation |
| All | varies | Follow NHTSA guidelines |
Exceptions to the Nevada Car Seat Laws
You’ve installed the car seat correctly, following the guidelines set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and the manufacturer’s instructions.
There are exceptions to Nevada’s car seat laws, including emergency vehicles and medical conditions with a doctor’s note. You must verify exceptions for compliance, prioritizing safety and proper restraint to avoid penalties.
A doctor’s note can exempt children with certain medical conditions or those who are too large for a standard car seat.
Penalties for Violations of the Car Seat Law
Violating Nevada’s car seat law can result in significant penalties, as the state takes child safety seriously.
You’ll face fines and community service for first violations. Repeat offenses incur higher fines, more community service, and potential license suspension.
Penalties for non-compliance also include child endangerment charges. Fines range from $100 to $1,000, and community service from 10 to 100 hours.
You may face license suspension for multiple violations, emphasizing the importance of complying with Nevada’s car seat law to avoid severe penalties.
Negligence and Defective Child Car Seats
Nevada’s car seat laws and penalties for non-compliance underscore the state’s commitment to child safety.
You should know that violating car seat laws doesn’t automatically indicate negligence. However, manufacturers can be held liable for defective car seats that cause child injuries, failing safety standards.
Retaining a car seat after an incident helps evaluate potential defects, supporting or defending against liability claims, and ensuring product safety, as approximately 12 million defective car seats have been recalled in the past decade.
Heatstroke Awareness and Prevention
You’ll learn about the heat risks associated with leaving children in vehicles, even on mild days, and how temperatures inside a parked car can rise significantly higher than the outside temperature.
As you consider car checks, you’ll understand the importance of verifying that no child is left behind in a vehicle, a simple step that can save lives.
You’ll also discover rescue tips, including Nevada’s law providing immunity to individuals who rescue a child from a hot car, emphasizing the need for timely intervention to prevent heat-related incidents.
Heat Risks
As you’re likely aware, heatstroke poses a significant threat to children left unattended in vehicles, and it’s essential to understand the risks involved.
You must check the back seat to prevent heatstroke, as a child’s body heats up 3 to 5 times faster than an adult’s, making them vulnerable.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration reports an average of 39 child heatstroke deaths in vehicles annually, emphasizing the need for prevention to avoid such accidents.
Car Checks
Several key factors contribute to heatstroke in vehicles, and it’s crucial to understand them to prevent such incidents.
You must conduct a car seat inspection, confirming proper installation and adherence to Nevada’s car seat requirements based on your child’s age.
Check the vehicle seat, and use a booster seat if necessary. This helps prevent serious injuries, as emphasized by safety organizations.
Always check the back seat to verify your child isn’t left behind, following Nevada’s guidelines for a safe vehicle environment.
Rescue Tips
One essential factor in preventing heatstroke incidents is being aware of the risks and knowing how to respond. You can use a reminder item to guarantee child safety.
| Booster Seats | Child Safety | Heatstroke |
|---|---|---|
| Required | Mandatory | Preventable |
| Nevada law | Car accident lawyers | Emergency vehicles |
| Reminder item | Child’s injuries | Awareness |
Guidelines for Protecting Children in Vehicles
When you’re driving with kids, it’s essential that you follow Nevada’s guidelines for protecting children in vehicles.
You must use booster seats for children aged 4 to 12, until they’re 57 inches tall or weigh 60 pounds, ensuring proper seat belt fit in the back seat.
Nevada law prioritizes children’s safety, setting height and weight limits for booster seats to reduce injury risks.
This boosts safety, and you should adhere to these rules for your children’s well-being.
Car Seat Inspection and Installation Resources
To guarantee your child’s car seat or booster seat is installed correctly, you’ll find various resources available in Nevada.
| Resource | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| NHTSA | Car seat finder | Proper fit |
| Car seat checkpoints | Free inspections | Safety updates |
| Local sites | Installation help | Compliance |
| Online tools | Recall notifications | Awareness |
| Trained staff | Detailed inspections | Peace of mind |
Prioritizing Child Safety on the Road
You’ve taken the first step in ensuring your child’s safety by exploring car seat inspection and installation resources in Nevada.
Now, prioritize child safety on the road by using booster seats correctly. Nevada law requires booster seats for children under 6, ensuring proper seat belt fit.
Place them in the back seat to minimize injury risk. Compliance reduces injury risk by up to 45% and avoids penalties, promoting child safety through proper use.
State-by-State Booster Seat Laws: Age/Weight Requirements, Rules & Penalties
| Alabama | Alabama requires children age 5 and under to ride in a child safety seat; booster seats are mandated for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age/weight limits are met. Penalties include fines for noncompliance. |
| Alaska | Alaska’s law mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height thresholds. Failure to comply can result in citations and fines. |
| Arizona | Arizona requires children under age 5 in appropriate child restraints; boosters are required until children reach height/weight guidelines. Violations may lead to fines. |
| Arkansas | Arkansas requires booster seats for children ages 4–8 who outgrow forward-facing seats until they meet height/weight requirements; noncompliance can lead to penalties. |
| California | California mandates booster seats for children under age 8 unless they are 4’9″ tall. Violations result in fines and may increase insurance costs. |
| Colorado | Colorado law requires boosters for children over forward-facing limits through age 8 or until height/weight thresholds are met. Fines apply for nonuse. |
| Connecticut | Connecticut requires booster seats for children under age 8 who have outgrown forward-facing seats. Penalties include fines for noncompliance. |
| Delaware | Delaware mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits up to age 8; infractions can lead to monetary penalties. |
| Florida | Florida requires children under age 6 to be in an appropriate child restraint; boosters are recommended until height/weight limits are met. Violations can result in fines. |
| Georgia | Georgia law requires boosters for children ages 4–7 who exceed forward-facing seat limits until they reach height/weight thresholds. Penalties include fines. |
| Hawaii | Hawaii mandates booster seats for children who have outgrown forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height/weight requirements; fines apply for nonuse. |
| Idaho | Idaho requires booster seats for children after forward-facing stage through age 7 or until height/weight thresholds are met. Noncompliance carries fines. |
| Illinois | Illinois law requires booster seats for children under age 8 unless they exceed height/weight limits; violations result in fines. |
| Indiana | Indiana mandates boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing seats through age 7 or until meeting height/weight standards; penalties include fines. |
| Iowa | Iowa requires booster seats for children ages 4–7 who exceed forward-facing stage until they reach height/weight limits; fines may be imposed. |
| Kansas | Kansas mandates booster seats for children who have outgrown forward-facing seats through age 8 or until height/weight limits are met; violations carry fines. |
| Kentucky | Kentucky law requires boosters for children over forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight criteria; infractions result in fines. |
| Louisiana | Louisiana mandates booster seats for children after the forward-facing stage up to age 8 or until proper height/weight is reached; fines apply. |
| Maine | Maine requires booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; noncompliance may lead to fines. |
| Maryland | Maryland law mandates boosters for children beyond forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight thresholds; penalties include fines. |
| Massachusetts | Massachusetts requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing stages until age 8 or height/weight limits; fines apply for violations. |
| Michigan | Michigan mandates booster seats for children after forward-facing stage through age 8 or until height/weight requirements are met; fines may be assessed. |
| Minnesota | Minnesota requires boosters for children who exceed forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; noncompliance results in fines. |
| Mississippi | Mississippi mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or until proper height/weight; violations carry fines. |
| Missouri | Missouri’s booster seat law requires usage for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 7 or height/weight thresholds; fines may apply. |
| Montana | Montana requires booster seats for children after forward-facing limits until age 7 or height/weight benchmarks; fines for noncompliance. |
| Nebraska | Nebraska mandates booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats through age 8 or until height/weight limits are met; penalties include fines. |
| New Hampshire | New Hampshire requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits up to age 7 or until height/weight thresholds apply; fines for violations. |
| New Jersey | New Jersey mandates booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing stages until age 8 or height/weight limits; noncompliance results in fines. |
| New Mexico | New Mexico requires booster seats after forward-facing limits through age 7 or height/weight thresholds; violations may lead to fines. |
| New York | New York’s booster seat law requires usage until age 8 or until height/weight limits are met. Penalties include fines and possible points. |
| North Carolina | North Carolina mandates booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines apply. |
| North Dakota | North Dakota requires booster seats after forward-facing stage through age 7 or until height/weight thresholds; penalties include fines. |
| Ohio | Ohio mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met; fines may be assessed. |
| Oklahoma | Oklahoma requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight benchmarks; fines apply. |
| Oregon | Oregon’s booster seat law mandates usage for children after forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight requirements; penalties include fines. |
| Pennsylvania | Pennsylvania requires boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight limits; fines apply for noncompliance. |
| Rhode Island | Rhode Island mandates boosters until age 8 or height/weight criteria are met. Violations may result in fines. |
| South Carolina | South Carolina requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight benchmarks; fines apply. |
| South Dakota | South Dakota mandates boosters for children after forward-facing stage until age 7 or height/weight limits; penalties include fines. |
| Tennessee | Tennessee requires booster seats for children who outgrow forward-facing limits until age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines may be imposed. |
| Texas | Texas mandates booster seats for children beyond forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight thresholds; violations result in fines. |
| Utah | Utah’s booster seat law requires usage until age 8 or until height/weight requirements are met; fines apply for violations. |
| Vermont | Vermont requires booster seats for children who exceed forward-facing seat limits until age 8 or height/weight benchmarks. Noncompliance carries fines and possible points. |
| Virginia | Virginia mandates booster seats until age 8 or until height/weight criteria; violations may lead to fines and points. |
| Washington | Washington requires boosters for children who outgrow forward-facing limits up to age 8 or height/weight limits; fines can be assessed. |
| West Virginia | West Virginia mandates booster seats until age 8 or height/weight thresholds are met; penalties include fines. |
| Wisconsin | Wisconsin requires booster seats for children beyond forward-facing limits through age 8 or height/weight criteria; fines may apply. |
| Wyoming | Wyoming’s booster seat law mandates usage for children who outgrow forward-facing seats until age 8 or height/weight limits; noncompliance results in fines. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Weight Requirement for a Booster Seat in Nevada?
You must use a booster seat until your child weighs 60 pounds or more, following Nevada’s child safety laws and booster seat regulations for safe family road trips.
Can My 7 Year Old Be Out of a Booster Seat?
You can consider removing your 7-year-old from a booster seat if they meet booster seat requirements, weighing at least 60 pounds, and pass child safety laws’ tests for car seat regulations.
At What Weight Can I Move My Child to a Booster Seat?
You can move your child to a booster seat at 40 pounds, following car seat guidelines and Nevada regulations to guarantee booster seat safety and compliance with child passenger laws.
Can a 10 Year Old Sit in the Front Seat in Nevada?
You’re absolutely allowed, but extremely ill-advised, to let a 10-year-old sit in the front seat, according to Nevada’s Front Seat Regulations and Child Passenger Safety guidelines under Nevada Traffic Laws.
Conclusion
You must prioritize child safety on the road, as “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” Nevada’s booster seat law is essential for protecting kids. You’ll guarantee their safety by following the regulations and guidelines. Remember, compliance is key to preventing injuries and saving lives, so always use approved booster seats correctly.

