The Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution X, commonly known as the Evo X, is a high-performance sports sedan with a legacy of power and precision. At the heart of this vehicle lies the 4B11T engine, a 2.0-liter inline-four turbocharged powerhouse designed for speed and reliability.
A critical element of the Evo X’s engine operation is its firing order, the sequence in which its cylinders fire to ensure efficient combustion and smooth performance.
This article explores the Evo X’s firing order, explains why it’s crucial, and provides insights on maintenance and troubleshooting. Whether you’re an Evo enthusiast, a mechanic, or a curious owner, this guide will help you understand this essential aspect of the 4B11T engine.
Quick Navigation
The Evo X Firing Order
The firing order for the Mitsubishi Evo X’s 4B11T engine is: 1-3-4-2
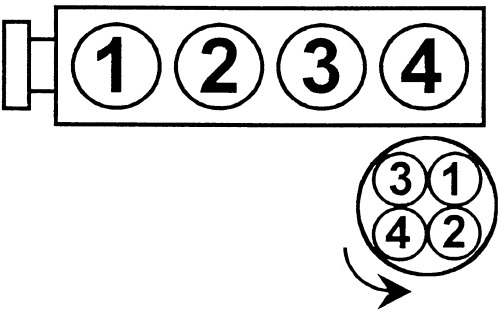
How the Firing Order Works
- Cylinder 1 Fires First: Located at the front of the engine, it starts the combustion cycle.
- Cylinder 3 Fires Second: Ignition moves to the third cylinder for balance.
- Cylinder 4 Fires Third: The rearmost cylinder fires next, continuing the sequence.
- Cylinder 2 Fires Last: The second cylinder completes the cycle before restarting with Cylinder 1.
This sequence alternates firing events across the cylinders to ensure smooth operation and reduce engine vibrations.
Why Mitsubishi Uses the 1-3-4-2 Firing Order
The 1-3-4-2 firing order is ideal for the inline-four configuration of the 4B11T engine. Here’s why:
- Engine Balance: Alternating firing events minimize vibrations and ensure stability.
- Heat Management: Spreads combustion heat evenly across all cylinders, preventing hot spots.
- Crankshaft Compatibility: Matches the crankshaft’s throw pattern for smooth rotation.
- Efficiency: Allows time for each cylinder to complete its intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust strokes.
What Is a Firing Order?
The firing order is the sequence in which an engine’s cylinders ignite their air-fuel mixture. This controlled combustion creates the power needed to rotate the crankshaft and propel the vehicle. In a four-cylinder engine like the Evo X’s 4B11T, the firing order is carefully engineered to optimize balance, efficiency, and power delivery.
Why the Firing Order Matters
- Smooth Operation: Reduces engine vibrations and ensures consistent power delivery.
- Efficiency: Ensures complete combustion for improved fuel economy and reduced emissions.
- Durability: Balances stress on the crankshaft and other components, extending engine life.
- Performance: Provides steady torque for smooth acceleration and precise handling.
Overview of the Evo X’s 4B11T Engine
The 4B11T is a 2.0-liter turbocharged inline-four engine, part of Mitsubishi’s Global Engine Manufacturing Alliance (GEMA) family. It replaced the 4G63 engine from previous Evo models, offering a more modern design with aluminum construction, variable valve timing, and improved turbocharging.
Key Features of the 4B11T Engine
- Inline-Four Configuration: Four cylinders arranged in a straight line.
- DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshafts): Improves airflow and valve control.
- MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic Control): Enhances efficiency and performance.
- Turbocharged: Equipped with a twin-scroll turbocharger for rapid boost response.
- Cylinder Numbering:
- Cylinders are numbered sequentially from the front of the engine to the rear:
- Cylinder 1 is closest to the timing chain (front).
- Cylinder 4 is closest to the transmission (rear).
- Cylinders are numbered sequentially from the front of the engine to the rear:
Identifying the Firing Order
To verify or adjust the firing order, you need to understand the cylinder layout and ignition system setup.
Cylinder Numbering
The cylinders are numbered sequentially from the front of the engine (timing chain) to the rear (transmission):
- Cylinder 1: Frontmost cylinder.
- Cylinder 4: Rearmost cylinder.
Ignition System
The Evo X’s 4B11T engine uses a coil-on-plug ignition system, which eliminates the need for spark plug wires. Each cylinder has its own ignition coil, controlled by the ECU (Engine Control Unit) to fire in the correct sequence.
Symptoms of an Incorrect Firing Order
An incorrect firing order can cause noticeable engine performance issues. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you identify and fix the problem before it causes further damage.
Common Symptoms
- Engine Misfires: Cylinders fire out of sequence, causing uneven power delivery.
- Rough Idling: Excessive vibrations or instability when the engine is idling.
- Power Loss: Reduced acceleration and sluggish performance.
- Backfiring: Combustion occurs in the intake or exhaust system due to improper timing.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Inefficient combustion leads to higher fuel usage and emissions.
Diagnosing and Fixing Firing Order Problems
If you suspect a firing order issue in your Evo X, follow these steps to diagnose and resolve it:
Diagnostic Steps
- Inspect Ignition Coils: Verify that each coil is connected to the correct cylinder.
- Check the ECU: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for error codes related to misfires or ignition timing.
- Perform a Compression Test: Ensure all cylinders have adequate compression for proper combustion.
- Examine Timing Components: Check the timing chain and camshaft alignment to ensure proper synchronization.
Fixing Common Issues
- Reconnect Ignition Coils: Ensure each coil is properly seated and aligned with its respective cylinder.
- Replace Faulty Components: Install new spark plugs or ignition coils if they are damaged or worn.
- Reprogram the ECU: If software issues are causing ignition problems, update or reset the ECU.
- Adjust Timing: Realign the timing chain and camshafts if they are out of sync.
Preventative Maintenance for Firing Order Reliability
Maintaining the correct firing order is essential for the performance and longevity of your Evo X’s 4B11T engine. Follow these preventative tips to ensure reliable operation:
Regular Inspections
- Inspect spark plugs and ignition coils for wear or damage.
- Check the timing chain and associated components for proper alignment and tension.
Use High-Quality Fuel
- Use premium gasoline to prevent carbon buildup on spark plugs and valves, ensuring efficient combustion.
Replace Components as Needed
- Replace spark plugs and ignition coils at intervals recommended by Mitsubishi.
- Use OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts to ensure compatibility and reliability.
Monitor Engine Performance
- Pay attention to changes in engine behavior, such as rough idling or power loss.
- Use a diagnostic scanner regularly to identify potential issues before they worsen.
Engines with Similar Firing Orders
FAQs About the Evo X Firing Order
Can I Change the Firing Order?
No, the firing order is determined by the engine’s design and crankshaft configuration. Altering it would require extensive modifications.
What Happens If the Firing Order Is Incorrect?
An incorrect firing order can cause misfires, backfiring, power loss, and potential damage to the engine’s internal components.
How Can I Verify the Firing Order?
Refer to the service manual, inspect ignition coil connections, and use diagnostic tools to confirm the sequence.
Conclusion
The 1-3-4-2 firing order is a critical aspect of the Mitsubishi Evo X’s 4B11T engine, ensuring smooth operation, balanced power delivery, and efficient combustion. Understanding and maintaining this sequence is essential for keeping your engine running at its peak performance, whether you’re on the street or the track.
By following proper maintenance practices, addressing issues promptly, and using high-quality components, you can enjoy the full potential of your Evo X. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, mastering the firing order is a vital step in caring for this legendary turbocharged engine.

